Decision making in an environment is a tool that helps the decision maker to make good decision despite the level of uncertainty.
Decision Making And Decision-Making Approaches In An Environment
Reviewing the concepts of decision making by those who have contributed heavily to the success of decision making in an environment
Research shows that it is inescapable fact of human conditions, that what we received for good or bad depends in part of what action we freely choose to take and also in part of circumstances beyond our control. Making decision is a very important thing that we do in every day living.
Decision-making is the study of identifying and choosing alternatives based on the values and preferences of the decision-maker and making a decision implies that there are alternative choices to be considered.
Dr. John Bukowski (2012), ”believed that one method we can use to help decide is the cut-off screening method” here the decision-maker predetermines a cut-off for each criterion.
Then the decision-maker goes through each criterion and eliminates any choice that doesn’t meet the cut-off. If more than one choice remain, the decision-maker could consider additional criterion or restrict the cut-off. If all choices have been eliminated, the decision maker can relax the cut-off. (Herold k; 2009) ”Certainty in decision-making environment implies that we know with 100 percent accuracy what the state of nature will be and what the expected outcome will be for each state of nature.
He also believed that decision-making under condition of certainty is the easiest case to work with because with certainty, the decision-makers assumed that all the necessary information are available to assist them in making the right decision and they can predict the outcome with high level of confidence”
Decision-making under condition of uncertainty and risk has been described as the most worrisome situation in life activity as the information needed to make good decision are not complete thereby throwing the decision-maker into cognitive reasoning with the application of mathematics and probability. Making choice under uncertainty and risk endowed with probability and with the help of decision-making criteria will help the decision-maker to make good decision and expect a better payoff.
”This risky condition can only be assumed base on information provided and probability that situation will occur or not.’ Human performance in decision-making terms has been the subject of active research from several perspectives. In cognitive point of view, the decision process must be regarded as a continuous process integrated in the interaction with the environment.
Decision-Making Under Certainty
Certainty is one the environment in which decision are made. In this environment, the decision-maker have all the complete and necessary information needed to make good decision in other to achieve good outcome. Under this condition, accurate and reliable information on which to base decision is available. The cause and effect relationships are known and the future is highly predictable.
Thus, if we have two or more choices to make decision from, the alternative that give the optimum result will be chosen. Example: Mr. John just move to Atlanta to work and he is looking for a place to rent. He had been offered with two alternative rental places(say) A and B. Rental place A is close to his work place and is within a working distance. Rental place B is a bit far from his workplace and required him to drive to work. Both rental fees are $200 per room. with the complete information above, Mr. John will be able to make a decision in a very certain condition.
Decision-Making Under Uncertainty
Making decision when you are uncertain of the condition is similar to lack of information that can help us to decide. In this type of environment, the decision-maker has the knowledge about the state of nature that happen but lack the knowledge about the probability of there occurrence.
In other to make good decision, the decision-maker has to judge and make the decision based on their experience. If they do not have such experience, they have to consult and seek advice from people who have more experience.
The insufficient data leads to more complex decision model which involves the use of scientific methods to exploit the available data. scientist like Hurwicz, Laplace, Salvage and Wald have contributed immensely in decision-making under uncertainty. Also, we consider maximax criterion in decision making.
Example: A restaurant that is famous for there chicken rice at Kentucky, they have been selling chicken rice for the past few years. Business has been good; however,they are thinking of expanding the business. Hence, they decided to try out selling Duck Rice. Since that would be first shop ever in Kentucky restaurant, the restaurant is not sure whether the people in Kentucky will accept Duck Rice as well? How much would they sell Duck Rice? Will Duck Rice be sold as the same price as Chicken Rice or cheaper? In this case, the restaurant are facing a time where they are making decision in an uncertain condition.
Economic Growth, Development and Unbalanced Growth
Maximax Criterion
This is one of the criterion used in decision making under condition of uncertainty that consider chosen the alternative that have high degree of occurrence in the payoff matrix. It provides the decision maker with optimistic criterion.
Wald Criterion
wald criterion is also known as maximin criterion which are pessimistic or conservative approach in decision making. this criterion assume that the worst will happen and the payoff with the smallest value may have the highest probability. Wald suggested that the decision maker examines only the minimum payoff of the alternatives and chooses the alternative whose outcome is least bad.
Salvage Criterion
Salvage is of the view that the decision maker regret the fact that he/she has adopted a wrong cause of action (alternative) resulting in an opportunity loss of payoff.
This criterion is also known as minimax regret criterion or opportunity loss criterion. thus, the decision maker should attempt to minimize regret before actually selecting a particular alternative. The regret corresponding to a particular payoff
R(ai,sj) is given by
R(ai,sj) = Rj(max)−R(ai,sj)
where Rj(max) is the column maximim.
The definition of regret above allow the decision maker to transform the payoff matrix into regret matrix. The salvage criterion suggested that the decision maker looks at the maximum regret of each alternative and select the one with smallest value.
Thus, if the decision alternative secures the best possible payoff for a given state of nature, the opportunity loss is equal to zero and that means that there is no regret. The opportunity loss is always non-negative quantity. Therefor, the higher the opportunity loss the greater the regret.
Laplace Criterion (Bayes Criterion)
Laplace criterion is also known as criterion of rationality. laplace suggested that since the probability associated with the occurrence is unknown, there is not enough information to conclude that this probability of there occurrence will be different and for that reason, we should assign equal probability to each of alternative.
This criterion is based upon principle of insufficient reason. Therefor, if there are n outcomes , the probability of each outcome will be 1 n. Using this probability, we calculate the the expected payoff for each alternative and select the alternative with the largest value.
This criterion is the first criterion to make explicit use of probability assignment regarding the likelihood of occurrence of the states of nature. As a result, it is the first to elementary model to use all the information available in the payoff matrix.
Hurwicz Criterion
Hurwicz is one of the scientist that contributed heavily in the decision making in an environment. Hurwicz is of the view that the decision maker should be intermediate in the decision making so as to accommodate optimistic and pessimistic attitude of the decision maker.
Hurwicz use the method of weighted average H to select the best decision among all alternatives. Here, the decision maker will be able to assign a weight (say) α which is called coefficient of optimism to each alternative according to the degree of optimistic or pessimistic attitude of the decision maker. where α lie between 0 ≤ α ≤ 1. If α = 1, it indicate total optimistic of the decision and it reduces to maximax criterion. If α = 0, it imply total pessimistic and reduces to maximin criterion(wald).
If we consider the weight α to be the degree of optimism, then the corresponding degree of pessimism is 1 – α and the hurwicz weighted average
H = α(rowmax) + 1-α(rowmin) for positive flow payoffs
H = α(rowmin) + 1-α(rowmax) for negative flow payoffs
Decision-Making Under Risk
Here, the decision-maker has incomplete information about the available alternatives but has good idea of the probability of the outcomes for each alternatives. Most business decision may have to undertake risk. This probability could be obtain from past record or simply subjective judgment of the decision-maker. Under risk, a good number of decision criterion are available which could be of help to the decision-maker
Example: A new skin product has been release to the market, it is a face cleaner called original face cleaner. It is a product commercialized to guarantee skin whitening in just several time of using.
There is no exact information that explain how the product help in improving the skin color and how long exactly it take to get the effect. However, due to the attractive price and the result promised, consumers decided to give the product a try. In this case, the consumers are making decision to buy the product under risk condition.
Expected Value Criterion
This criterion requires the computation of the expected value of each alternatives which is the sum of the weighted payoffs for that alternative and the weight are the probability assigned to the state of nature. It is also called the expected monetary value(EMV) criterion.
Expected Opportunity Loss
Expected opportunity loss (EOL) also known as expected value of regret is a statistical calculation used primarily in the business field to help determine optimal course of action. doing business is full of decision making .
Any decision consists of a choice between two or more event. For each event, there are two or more possible courses of action that you might take. Calculating EOL is an organized way of using a mathematical model these choices and outcomes to take the most profitable decision. AN alternative approach to maximize the EMV approach is to minimize the EOL.
EOL represent the amount by which maximum possible profit will be reduced under various possible stock actions. The course of action that minimizes these losses or reduction is the optimal decision alternative.
Expected Value Of Perfect Information(EVPI)
This is where we make use of the idea of decision making under certainty. suppose that although you couldnt control the future , you could foresee the future with perfect accuracy. Thats what certainty is all about. If you could foresee the future perfectly, then you would have perfect information. perfect information is certainly the very best kind of information.
Imperfect information can never be valuable. It is certainly too bad that perfect information doesnt really exist. Thus, the expected value of perfect information is the maximum amount you will be willing to pay for additional information about a decision problem.
Steps In Decision-Making Approach
Generally, decision-making approach involves four steps. We shall introduced these steps by considering a manufacturing industry that is thinking of several alternative methods to increase its production to meet the increasing market demand.
STEP 1:
List all the viable alternatives. In other to make good decision, the decisionmaker has to list all the viable alternatives that can be considered in the decision. These alternatives are also called actions or strategies and they are under the control of decision-maker. For instance, the manufacturing industry may have only three alternatives, which are:
- 1. expand the current plant
2. construct new plant
3. subcontract production for extra demand
STEP 2:
Identify the expected future events. The future event are also called state of nature or outcomes which are not under the control of decision-makers. The decision-maker is to list all the future events that may occur. Often, it is possible to identify most of the events that will occur but difficult to identify which particular event that can occur, out of this future events, only one will occur. For the manufacturing industry the greatest uncertainty will be about the product demand. The state of nature related to the demand may be:
- 1. High demand
2. low demand
3. moderate demand
4. No demand
STEP 3:
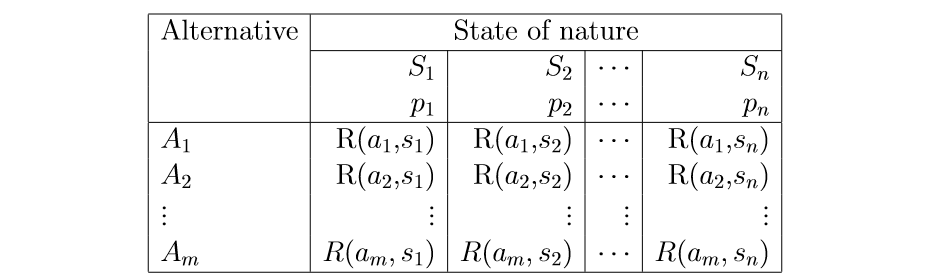
Construct a payoff table. The step three is to construct a payoff table(table representing profit or benefit) for each possible combination of alternative and state of nature.
- A is the decision alternatives
- S is the state of nature
- P is the probability applicable to
- R is the payoff (rewards) obtain by choosing alternative Ai if state of nature Sj occurs
STEP 4:
Select the optimum decision criterion. Finally, the decision-maker will choose criterion whose result is the largest payoff.
Roles Information Technology Advisors Play In Businesses
Decision making has been proven to be one of the action that human need to adopt in every day life in other to succeed in most of the activities been carried out on daily basis. Research shows that it is inescapable fact of human condition that what we received for good or bad depends mostly on the type of decision we freely choose to make.
In decision making, individual decision maker have to choose one of several alternatives with complete information about there outcomes, but lacks the information or data about the probability of the various state of nature. For the fact that decision making happen to be one of the top most priority in our lives, business and so many other activity, decision making in an environment which are certainty, uncertainty and risk have been a subject of discourse in other to achieve optimum result.
Because of uncertainty that exist in decision making, the decision maker find it difficult to make a good choice but with the help of decision making criteria, the decision maker can always overcome complexity of decision making.
Written by
(BSc Mathematics)